

The IP addresses must be in the same subnet.
 If an ARP entry does not exist, the switch sends an ARP query and tries to resolve the IP address. If an ARP entry exists for the specified IP address, the switch uses the associated MAC address and identifies the physical path. When you specify the IP addresses, the switch uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to associate the IP addresses with the corresponding MAC addresses and the VLAN IDs. The traceroute mac ip command output shows the Layer 2 path when the specified source and destination IP addresses are in the same subnet. This feature is not supported in Token Ring VLANs. The Layer 2 traceroute feature is not supported when multiple devices are attached to one port through hubs (for example, multiple CDP neighbors are detected on a port). The traceroute mac command output shows the Layer 2 path when the specified source and destination addresses belong to the same VLAN. Layer 2 traceroute supports only unicast traffic. The maximum number of hops identified in the path is ten.
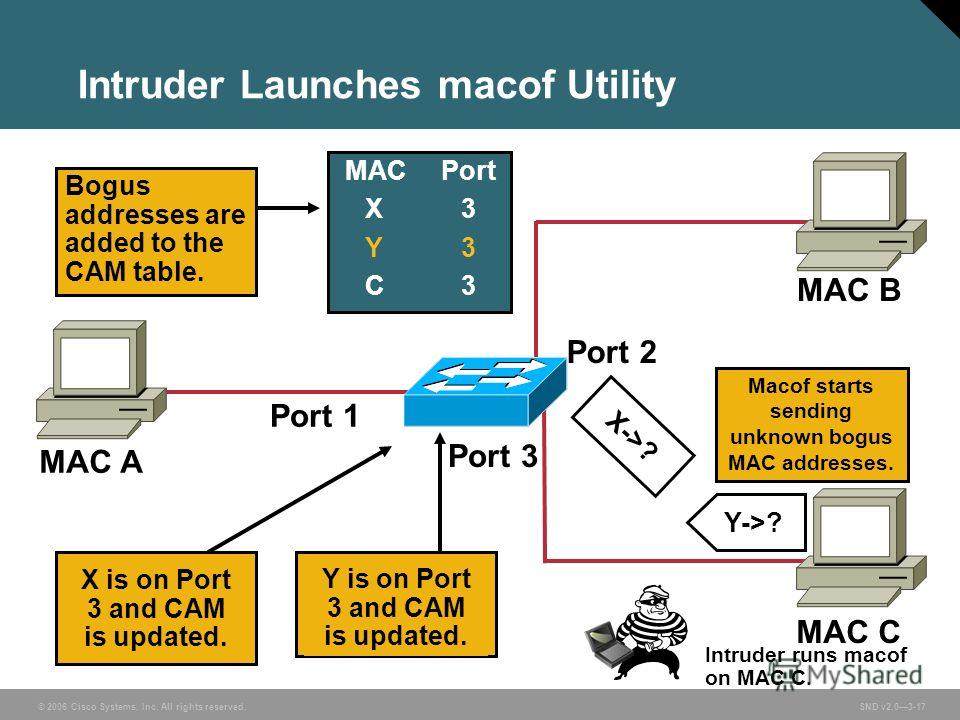
If an ARP entry does not exist, the switch sends an ARP query and tries to resolve the IP address. If an ARP entry exists for the specified IP address, the switch uses the associated MAC address and identifies the physical path. When you specify the IP addresses, the switch uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to associate the IP addresses with the corresponding MAC addresses and the VLAN IDs. The traceroute mac ip command output shows the Layer 2 path when the specified source and destination IP addresses are in the same subnet. This feature is not supported in Token Ring VLANs. The Layer 2 traceroute feature is not supported when multiple devices are attached to one port through hubs (for example, multiple CDP neighbors are detected on a port). The traceroute mac command output shows the Layer 2 path when the specified source and destination addresses belong to the same VLAN. Layer 2 traceroute supports only unicast traffic. The maximum number of hops identified in the path is ten. 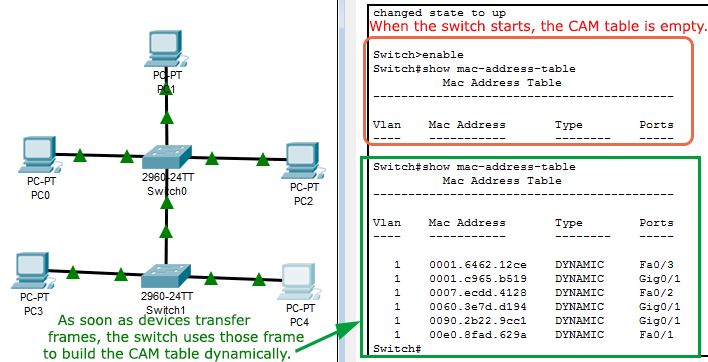 When the switch detects a device in the Layer 2 path that does not support Layer 2 traceroute, the switch continues to send Layer 2 trace queries and lets them time out. For Layer 2 traceroute to function properly, Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) must be enabled on all the switches in the network. Source not directly connected, tracing source. … and to have more detail about the trace use the ‘detail’ option: Ciscozine-SW1#traceroute mac ip 192.168.0.4 192.168.0.6 detail In the first case, use the command ‘traceroute mac 0019.9955.0f60 0b’ Ciscozine-SW1#traceroute mac 0019.9955.0f60 0b You have two options to find the path between two hosts: Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 6 Suppose to have two host (192.168.0.4, 192.168.0.6) and you would find the layer2 path using the Ciscozine-SW1 Switch.īelow the MAC address table and the ARP table of the Ciscozine-SW1 switch: Ciscozine-SW1#sh mac-address-table dynamic See you the example to understand how this feature works. If you specify source and destination addresses that belong to different VLANs, the Layer 2 path is not identified, and an error message appears. The traceroute mac command output shows the Layer2 path when the specified source and destination addresses belong to the same VLAN.
When the switch detects a device in the Layer 2 path that does not support Layer 2 traceroute, the switch continues to send Layer 2 trace queries and lets them time out. For Layer 2 traceroute to function properly, Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) must be enabled on all the switches in the network. Source not directly connected, tracing source. … and to have more detail about the trace use the ‘detail’ option: Ciscozine-SW1#traceroute mac ip 192.168.0.4 192.168.0.6 detail In the first case, use the command ‘traceroute mac 0019.9955.0f60 0b’ Ciscozine-SW1#traceroute mac 0019.9955.0f60 0b You have two options to find the path between two hosts: Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 6 Suppose to have two host (192.168.0.4, 192.168.0.6) and you would find the layer2 path using the Ciscozine-SW1 Switch.īelow the MAC address table and the ARP table of the Ciscozine-SW1 switch: Ciscozine-SW1#sh mac-address-table dynamic See you the example to understand how this feature works. If you specify source and destination addresses that belong to different VLANs, the Layer 2 path is not identified, and an error message appears. The traceroute mac command output shows the Layer2 path when the specified source and destination addresses belong to the same VLAN. 
To do it, Cisco has implemented a good tool: traceroute mac. In a Data Center, it is often required to find a host and the layer2 path. Routers decrement this parameter and discard a packet when the TTL value has reached zero, returning an ICMP error message (ICMP Time Exceeded) to the sender. Tracing the intermediate routers traversed involves control of the time-to-live (TTL) Internet Protocol parameter. Traceroute sends a sequence of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets addressed to a destination host. Here is the example with the mac adddresses swapped issued from the same switch on the right side: RL-SW-5-3750-TS-QinQtrace mac 0007.0eae.4420 0050.56ba.5bed. Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1īut since I could not see IP addresses getting associated to the MAC addresses, I did a shut / no shut on the port but have not been able to see the MAC address since.Traceroute is a tool for measuring the route path and transit times of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. You can do this from any switch having access to the VLAN the two mac addresses are connected to. I was able to see that a couple of hours back The configuration on the interfaces are as follows:ĭescription # ALert Logic monitor port #īut I cannot see them on the MAC address table I have two devices connected on two ports of the switch Gi1/0/41 and Gi1/0/42. I am experiencing a strange problem and would be grateful to have some advice on this.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
